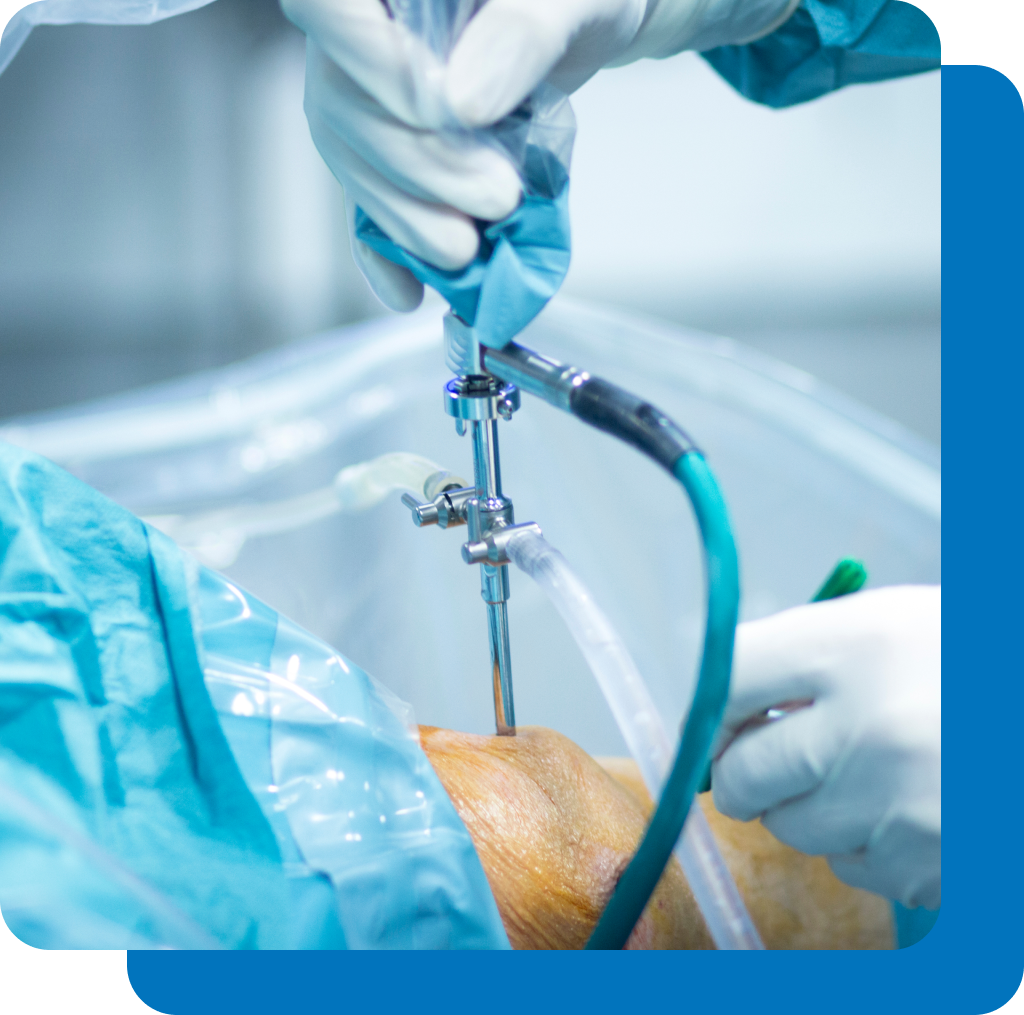
Laparoscopic surgery is a surgical technique used to examine organs in the abdominal area. It is also used for pelvic organ surgery in women. A laparoscope (thin lighted tube) with a video camera is used. It is inserted into a small incision in the abdomen. The images from the video camera are shown on a computer monitor.
One of the advantages of laparoscopic surgery is its minimality. This means that a very small incision is made in the abdomen. Because of this, laparoscopic surgery often has a shorter recovery time and is less invasive than traditional surgery.
A laparoscopy is a procedure in which a small sample of tissue is taken for testing (known as a biopsy). A laparoscopy can also remove organs, including the appendix (an appendectomy) or gallbladder (a cholecystectomy). Laparoscopic surgery is the choice in Hernia repair and fundoplication.
In Gynecological procedures especially for those associated with infertility, laparoscope is used in procedures like ovarian cystectomy, ovarian drilling, and much more.
Laparoscopy is also used for diagnostic purpose prior to IUI/IVF procedures to detect tubal defects etc.
No. 200/A, 9TH Cross,
HMT Layout, R.T. Nagar,
Bangalore - 560032,
Karnataka, India.
info@poornimahospital.com
08023557272
08023557273
08023336455
08023337272
0802336455
9986007272
No. 200/A, 9TH Cross,
HMT Layout, R.T Nagar,
Bangalore - 560032,
Karnataka, India.
info@poornimahospital.com
80 2333 7272 / 73

info@poornimahospital.com
Phone : 80 2333 7272 / 73